Identify the missing statement or reason to complete the two-column proof. Type the letter of your answer in each blank.
| Given: | Quadrilateral ABCD with and |
| Prove: | Quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram. |
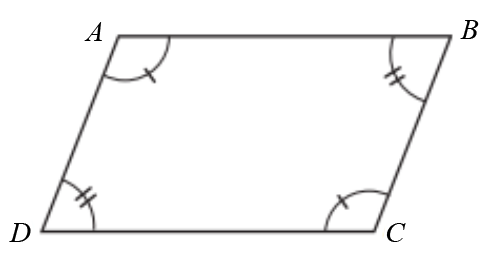
Choices:
| a. | |
| b. | Substitution Property of Equality |
| c. | and are supplementary. |
| d. | |
| e. | |
| f. | Definition of parallelogram |
| g. | Definition of same-side interior angles |
| h. | and are same-side interior angles. |
| i. | Definition of supplementary angles |
| j. | Division Property of Equality |
| k. | Converse of Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem |
| l. | The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex polygon with n sides is equal to |
Proof:
| Statements | Reasons | ||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|


